Linear interpolation(线性插值)
已知中P1点和P2点,坐标分别为(x1, y1)、(x2, y2),要计算 [x1, x2] 区间内某一位置 x 在直线上的y值
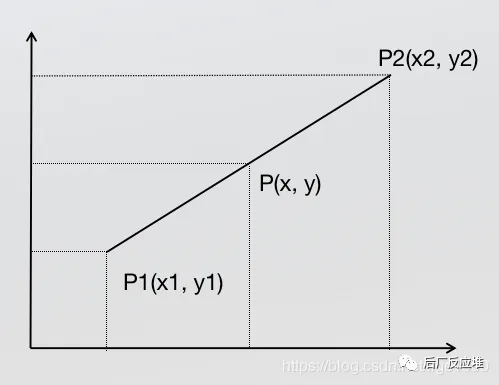
根据初中的知识,2点求一条直线公式(这是双线性插值所需要的唯一的基础公式)
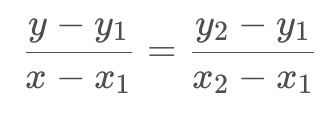
经过简单整理成下面的格式:
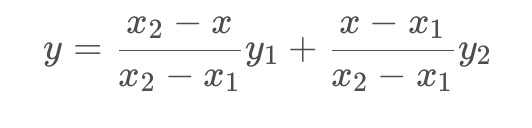
这里没有写成经典的AX+B的形式,因为这种形式从权重的角度更好理解。
首先看分子,分子可以看成x与x1和x2的距离作为权重,这也是很好理解的,P点与P1、P2点符合线性变化关系,所以P离P1近就更接近P1,反之则更接近P2。
现在再把公式中的分式看成一个整体,原式可以理解成y1与y2是加权系数,如何理解这个加权,要返回来思考一下,咱们先要明确一下根本的目的:咱们现在不是在求一个公式,而是在图像中根据2个点的像素值求未知点的像素值。这样一个公式是不满足咱们写代码的要求的。 现在根据实际的目的理解,就很好理解这个加权了,y1与y2分别代表原图像中的像素值,上面的公式可以写成如下形式:
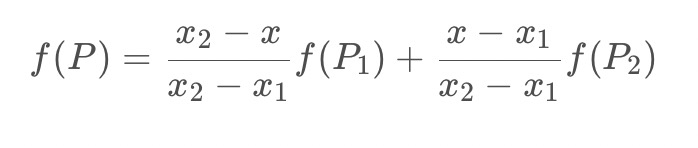
nearest neighbor(最近邻插值)
Bilinear interpolation(双线性插值)
已知Q11(x1,y1)、Q12(x1,y2)、Q21(x2,y1)、Q22(x2,y2),求其中点P(x,y)的值。
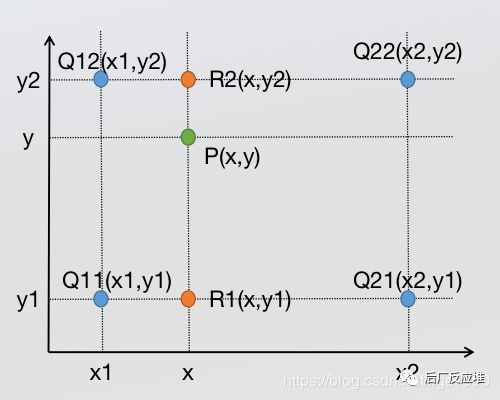
前面介绍过双线性插值是分别在两个方向计算了共3次单线性插值,如图所示,先在x方向求2次单线性插值,获得R1(x, y1)、R2(x, y2)两个临时点,再在y方向计算1次单线性插值得出P(x, y)(实际上调换2次轴的方向先y后x也是一样的结果)。 1.x方向单线性插值 直接带入前一步单线性插值最后的公式
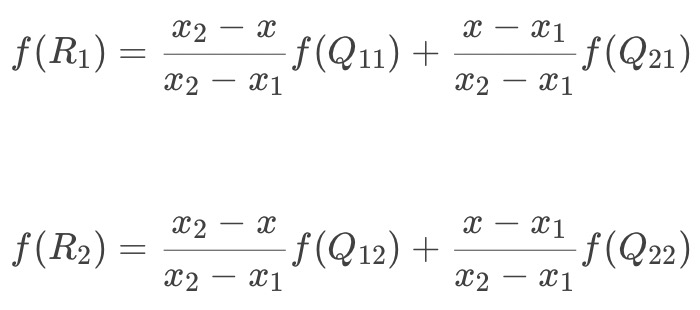
2.y方向单线性插值
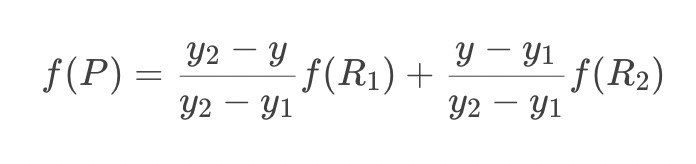
将第一步结果带入第二步
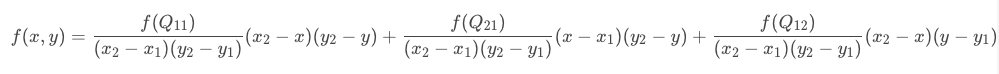
回顾一下上面双线性插值对应关系的图,不难发现,在计算中有这样的关系:
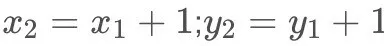
那么上面的公式中的分母全都为1,如下:
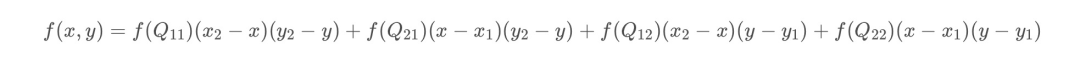
在有些资料中,会写成权重的形式,上面的展开式是下面的权重表达式的正确求法
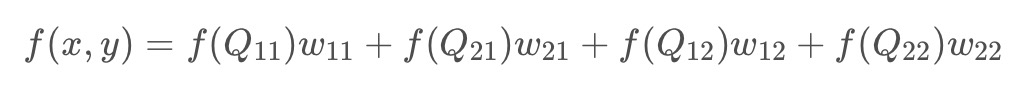
cubic interpolation(三次插值)
//权重计算函数
//输入:x:自变量的值 times: 图片超分倍数
//返回值:W(x)计算之后的值
double W(int x,int times){
x=std::abs(x);
//OpenCV 中给的是 -0.75
double a=-0.75;
double abs_=std::abs((double)x/(double)times);
if(x>=2*times) return 0.0;
else if(x>times){
double ans=a*(abs_)*(abs_)*(abs_)-5*a*(abs_)*(abs_)+8*a*(abs_)-4*a;
return ans;
}
else{
double ans=(a+2)*(abs_)*(abs_)*(abs_)-(a+3)*(abs_)*(abs_)+1;
return ans;
}
//不会执行到这里的,哈哈
return -1.0f;
}
//双三次插值
//输入:原图像(单通道),超分倍数
//返回值:超分后的图像
cv::Mat biCubicInterp(const cv::Mat &src, int times){
cv::Mat dst=cv::Mat::zeros(cv::Size(src.cols*times,src.rows*times),CV_8UC1);
for(int i=0;i<dst.rows;i++){
for(int j=0;j<dst.cols;j++){
double val=0.0;
//利用周围16个像素点计算插值
for(int r=-1;r<=2;r++){
//如果参考点超出图像范围,则舍弃
if(i/times+r<0 || i/times+r>=src.rows) continue;
for(int c=-1;c<=2;c++){
//如果参考点超出图像范围,则舍弃
if(j/times+c<0 || j/times+c>=src.cols) continue;
val+=(src.at<uchar>(i/times+r,j/times+c)*W(i%times-r*times,times)*W(j%times-c*times,times));
}
}
//防止越界溢出
if(val>255) val=255;
if(val<0) val=-val;
dst.at<uchar>(i,j)=(unsigned char)val;
}
}
return dst;
}
BiCubic interpolation(双三次插值)
假设源图像A大小为mn,缩放K倍后的目标图像B的大小为MN,即K=M/m。A的每一个像素点是已知的,B是未知的,我们想要求出目标图像B中每一像素点(X,Y)的值,必须先找出像素(X,Y)在源图像A中对应的像素(x,y),再根据源图像A距离像素(x,y)最近的16个像素点作为计算目标图像B(X,Y)处像素值的参数,利用BiCubic基函数求出16个像素点的权重,图B像素(x,y)的值就等于16个像素点的加权叠加。
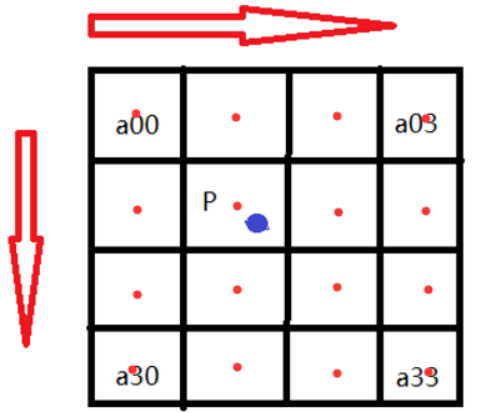
根据比例关系x/X=m/M=1/K,我们可以得到B(X,Y)在A上的对应坐标为A(x,y)=A(X*(m/M),Y*(n/N))=A(X/K,Y/K)。如图所示P点就是目标图像B在(X,Y)处对应于源图像A中的位置,P的坐标位置会出现小数部分,所以我们假设 P的坐标为P(x+u,y+v),其中x,y分别表示整数部分,u,v分别表示小数部分(蓝点到a11方格中红点的距离)。那么我们就可以得到如图所示的最近16个像素的位置,在这里用a(i,j)(i,j=0,1,2,3)来表示,如上图。
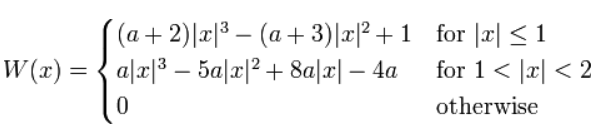
其中,a取-0.5,BiCubic函数具有如下形状:
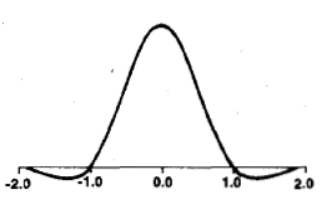
我们要做的就是求出BiCubic函数中的参数x,从而获得上面所说的16个像素所对应的权重W(x)。BiCubic基函数是一维的,而像素是二维的,所以我们将像素点的行与列分开计算。BiCubic函数中的参数x表示该像素点到P点的距离,例如a00距离P(x+u,y+v)的距离为(1+u,1+v),因此a00的横坐标权重i_0=W(1+u),纵坐标权重j_0=W(1+v),a00对B(X,Y)的贡献值为:(a00像素值)* i_0* j_0。因此,a0X的横坐标权重分别为W(1+u),W(u),W(1-u),W(2-u);ay0的纵坐标权重分别为W(1+v),W(v),W(1-v),W(2-v);B(X,Y)像素值为:
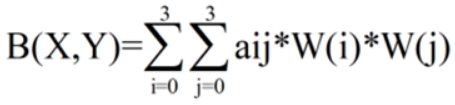
对待插值的像素点(x,y)(x和y可以为浮点数),取其附近的4x4邻域点(xi,yj), i,j = 0,1,2,3。按如下公式进行插值计算:
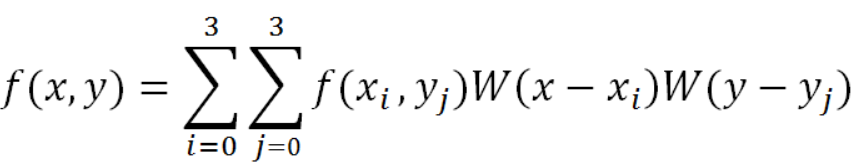
Matlab实现代码
%双三次插值具体实现
clc,clear;
fff=imread('E:\Documents\BUPT\DIP\图片\lena.bmp');
ff =rgb2gray(fff);%转化为灰度图像
[mm,nn]=size(ff); %将图像隔行隔列抽取元素,得到缩小的图像f
m=mm/2;
n=nn/2;
f =zeros(m,n);
for i=1:m
for j=1:n
f(i,j)=ff(2*i,2*j);
end
end
k=5; %设置放大倍数
bijiao1 =imresize(f,k,'bilinear');%双线性插值结果比较
bijiao =uint8(bijiao1);
a=f(1,:);
c=f(m,:); %将待插值图像矩阵前后各扩展两行两列,共扩展四行四列
b=[f(1,1),f(1,1),f(:,1)',f(m,1),f(m,1)];
d=[f(1,n),f(1,n),f(:,n)',f(m,n),f(m,n)];
a1=[a;a;f;c;c];
b1=[b;b;a1';d;d];
ffff=b1';
f1=double(ffff);
g1 =zeros(k*m,k*n);
fori=1:k*m %利用双三次插值公式对新图象所有像素赋值
u=rem(i,k)/k;
i1=floor(i/k)+2;
A=[sw(1+u) sw(u) sw(1-u) sw(2-u)];
for j=1:k*n
v=rem(j,k)/k;
j1=floor(j/k)+2;
C=[sw(1+v);sw(v);sw(1-v);sw(2-v)];
B=[f1(i1-1,j1-1) f1(i1-1,j1) f1(i1-1,j1+1)f1(i1-1,j1+2)
f1(i1,j1-1) f1(i1,j1) f1(i1,j1+1) f1(i1,j1+2)
f1(i1+1,j1-1) f1(i1+1,j1) f1(i1+1,j1+1) f1(i1+1,j1+2)
f1(i1+2,j1-1) f1(i1+2,j1) f1(i1+2,j1+1)f1(i1+2,j1+2)];
g1(i,j)=(A*B*C);
end
end
g=uint8(g1);
imshow(uint8(f));title('缩小的图像'); %显示缩小的图像
figure,imshow(ff);title('原图'); %显示原图像
figure,imshow(g);title('双三次插值放大的图像'); %显示插值后的图像
figure,imshow(bijiao);title('双线性插值放大结果'); %显示插值后的图像
mse=0;
ff=double(ff);
g=double(g);
ff2=fftshift(fft2(ff)); %计算原图像和插值图像的傅立叶幅度谱
g2=fftshift(fft2(g));
figure,subplot(1,2,1),imshow(log(abs(ff2)),[8,10]);title('原图像的傅立叶幅度谱');
subplot(1,2,2),imshow(log(abs(g2)),[8,10]);title('双三次插值图像的傅立叶幅度谱');
基函数代码:
functionA=sw(w1)
w=abs(w1);
ifw<1&&w>=0
A=1-2*w^2+w^3;
elseifw>=1&&w<2
A=4-8*w+5*w^2-w^3;
else
A=0;
end
C++实现代码
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <fstream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
#define PI 3.14159265
float BiCubicPoly(float x);
void MyScaleBiCubicInter(Mat& src, Mat& dst, float TransMat[3][3]);
/**
* @function main
*/
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
// load image
char* imageName = "images/Lenna_256.png";
Mat image;
image = imread(imageName,1);
if(!image.data)
{
cout << "No image data" << endl;
return -1;
}
// show image
namedWindow("image", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow("image", image);
Mat dst;
float transMat[3][3] = { {2.0, 0, 0}, {0, 2.0, 0}, {0, 0, 1} };
MyScaleBiCubicInter(image, dst, transMat);
namedWindow("out_image", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow("out_image", dst);
imwrite("Lenna_scale_biCubic2.jpg", dst);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
float BiCubicPoly(float x)
{
float abs_x = abs(x);
float a = -0.5;
if( abs_x <= 1.0 )
{
return (a+2)*pow(abs_x,3) - (a+3)*pow(abs_x,2) + 1;
}
else if( abs_x < 2.0 )
{
return a*pow(abs_x,3) - 5*a*pow(abs_x,2) + 8*a*abs_x - 4*a;
}
else
return 0.0;
}
void MyScaleBiCubicInter(Mat& src, Mat& dst, float TransMat[3][3])
{
CV_Assert(src.data);
CV_Assert(src.depth() != sizeof(uchar));
// calculate margin point of dst image
float left = 0;
float right = 0;
float top = 0;
float down = 0;
float x = src.cols * 1.0f;
float y = 0.0f;
float u1 = x * TransMat[0][0] + y * TransMat[0][1];
float v1 = x * TransMat[1][0] + y * TransMat[1][1];
x = src.cols * 1.0f;
y = src.rows * 1.0f;
float u2 = x * TransMat[0][0] + y * TransMat[0][1];
float v2 = x * TransMat[1][0] + y * TransMat[1][1];
x = 0.0f;
y = src.rows * 1.0f;
float u3 = x * TransMat[0][0] + y * TransMat[0][1];
float v3 = x * TransMat[1][0] + y * TransMat[1][1];
left = min( min( min(0.0f,u1), u2 ), u3);
right = max( max( max(0.0f,u1), u2 ), u3);
top = min( min( min(0.0f,v1), v2 ), v3);
down = max( max( max(0.0f,v1), v2 ), v3);
// create dst image
dst.create(int(abs(right-left)), int(abs(down-top)), src.type());
CV_Assert( dst.channels() == src.channels() );
int channels = dst.channels();
int i,j;
uchar* p;
uchar* q0;
uchar* q1;
uchar* q2;
uchar* q3;
for( i = 0; i < dst.rows; ++i)
{
p = dst.ptr<uchar>(i);
for ( j = 0; j < dst.cols; ++j)
{
//
x = (j+left)/TransMat[0][0] ;
y = (i+top)/TransMat[1][1] ;
int x0 = int(x) - 1;
int y0 = int(y) - 1;
int x1 = int(x);
int y1 = int(y);
int x2 = int(x) + 1;
int y2 = int(y) + 1;
int x3 = int(x) + 2;
int y3 = int(y) + 2;
if( (x0 >= 0) && (x3 < src.cols) && (y0 >= 0) && (y3 < src.rows) )
{
q0 = src.ptr<uchar>(y0);
q1 = src.ptr<uchar>(y1);
q2 = src.ptr<uchar>(y2);
q3 = src.ptr<uchar>(y3);
float dist_x0 = BiCubicPoly(x-x0);
float dist_x1 = BiCubicPoly(x-x1);
float dist_x2 = BiCubicPoly(x-x2);
float dist_x3 = BiCubicPoly(x-x3);
float dist_y0 = BiCubicPoly(y-y0);
float dist_y1 = BiCubicPoly(y-y1);
float dist_y2 = BiCubicPoly(y-y2);
float dist_y3 = BiCubicPoly(y-y3);
float dist_x0y0 = dist_x0 * dist_y0;
float dist_x0y1 = dist_x0 * dist_y1;
float dist_x0y2 = dist_x0 * dist_y2;
float dist_x0y3 = dist_x0 * dist_y3;
float dist_x1y0 = dist_x1 * dist_y0;
float dist_x1y1 = dist_x1 * dist_y1;
float dist_x1y2 = dist_x1 * dist_y2;
float dist_x1y3 = dist_x1 * dist_y3;
float dist_x2y0 = dist_x2 * dist_y0;
float dist_x2y1 = dist_x2 * dist_y1;
float dist_x2y2 = dist_x2 * dist_y2;
float dist_x2y3 = dist_x2 * dist_y3;
float dist_x3y0 = dist_x3 * dist_y0;
float dist_x3y1 = dist_x3 * dist_y1;
float dist_x3y2 = dist_x3 * dist_y2;
float dist_x3y3 = dist_x3 * dist_y3;
switch(channels)
{
case 1:
{
break;
}
case 3:
{
p[3*j] = (uchar)(q0[3*x0] * dist_x0y0 +
q1[3*x0] * dist_x0y1 +
q2[3*x0] * dist_x0y2 +
q3[3*x0] * dist_x0y3 +
q0[3*x1] * dist_x1y0 +
q1[3*x1] * dist_x1y1 +
q2[3*x1] * dist_x1y2 +
q3[3*x1] * dist_x1y3 +
q0[3*x2] * dist_x2y0 +
q1[3*x2] * dist_x2y1 +
q2[3*x2] * dist_x2y2 +
q3[3*x2] * dist_x2y3 +
q0[3*x3] * dist_x3y0 +
q1[3*x3] * dist_x3y1 +
q2[3*x3] * dist_x3y2 +
q3[3*x3] * dist_x3y3 ) ;
p[3*j+1] = (uchar)(q0[3*x0+1] * dist_x0y0 +
q1[3*x0+1] * dist_x0y1 +
q2[3*x0+1] * dist_x0y2 +
q3[3*x0+1] * dist_x0y3 +
q0[3*x1+1] * dist_x1y0 +
q1[3*x1+1] * dist_x1y1 +
q2[3*x1+1] * dist_x1y2 +
q3[3*x1+1] * dist_x1y3 +
q0[3*x2+1] * dist_x2y0 +
q1[3*x2+1] * dist_x2y1 +
q2[3*x2+1] * dist_x2y2 +
q3[3*x2+1] * dist_x2y3 +
q0[3*x3+1] * dist_x3y0 +
q1[3*x3+1] * dist_x3y1 +
q2[3*x3+1] * dist_x3y2 +
q3[3*x3+1] * dist_x3y3 ) ;
p[3*j+2] = (uchar)(q0[3*x0+2] * dist_x0y0 +
q1[3*x0+2] * dist_x0y1 +
q2[3*x0+2] * dist_x0y2 +
q3[3*x0+2] * dist_x0y3 +
q0[3*x1+2] * dist_x1y0 +
q1[3*x1+2] * dist_x1y1 +
q2[3*x1+2] * dist_x1y2 +
q3[3*x1+2] * dist_x1y3 +
q0[3*x2+2] * dist_x2y0 +
q1[3*x2+2] * dist_x2y1 +
q2[3*x2+2] * dist_x2y2 +
q3[3*x2+2] * dist_x2y3 +
q0[3*x3+2] * dist_x3y0 +
q1[3*x3+2] * dist_x3y1 +
q2[3*x3+2] * dist_x3y2 +
q3[3*x3+2] * dist_x3y3 ) ;
float thre = 198.0f;
if( (abs(p[3*j]-q1[3*x1]) > thre) || (abs(p[3*j+1]-q1[3*x1+1]) > thre) ||
(abs(p[3*j+2]-q1[3*x1+2]) > thre) )
{
p[3*j] = q1[3*x1];
p[3*j+1] = q1[3*x1+1];
p[3*j+2] = q1[3*x1+2];
}
break;
}
}
}
}
}
双三次插值(BiCubic插值)_bicubic函数_咖喱姬姬的博客-CSDN博客
图像放大并进行BiCubic插值 Matlab/C++代码_bicubic函数_Bicelove的博客-CSDN博客
插值(五)Bicubic interpolation(双三次插值)_双三次插值 知乎_怎么会有不写代码的小朋友呢的博客-CSDN博客
OpenCV图像缩放插值之BiCubic双三次插值_resize怎么改成双三次_对望小秘的博客-CSDN博客
代码
